Artifact: Analysis Class
Analysis Class |
Analysis classes represent an early conceptual model for ‘things in the system which have responsibilities and behavior’. |
| UML representation: | Class, stereotyped as <<boundary>>, <<entity>> or <<control>>. |
| Worker: | Designer |
| More information: | Guidelines: Analysis Class |
Purpose 
The following people use the analysis class:
- Designers use analysis classes to capture a ‘first-draft’, rough-cut of the object model of the system.
Properties 
Property Name |
Brief Description |
UML Representation |
| name | the name of the class | attribute |
| description | a brief description of the role of the class in the system | attribute |
| responsibilities | a listing of the responsibilities of the class | attribute |
| attributes | the attributes of the class | attribute |
Timing 
Analysis classes are created during Activity: Use Case Analysis. See Artifact: Analysis Model for a discussion of their continued maintenance.
Responsibility 
A designer is responsible for the integrity of the analysis class, ensuring that:
- It is complete and logically consistent.
- That all information (see properties above) is captured and is correct.
Tailoring 
The analysis classes, taken together, represent an early conceptual model of the system. This conceptual model evolves quickly and remains fluid for some time as different representations and their implications are explored. Formal documentation can impede this process, so be careful how much energy you expend on maintaining this ‘model’ in a formal sense; you can waste a lot of time polishing a model which is largely expendable. Analysis classes rarely survive into the design unchanged. Many of them represent whole collaborations of objects, often encapsulated by subsystems.
Usually, simple note-cards, such as the example below, are sufficient (this is based on the well-known CRC Card technique). On the front side of the card, capture the name and description of the class. An example for a Course in a course registration system is listed below:
| Class Name | Course | |
Description |
The Course is responsible for maintaining information about a set of course sections having a common subject, requirements and syllabus. | |
| Responsibilities | To maintain information about the course. | |
| Attributes | Description | Type |
| Course Title | The name of the course | string |
| Description | A short description of the course | string |
On the back of the card, draw a diagram of the class:
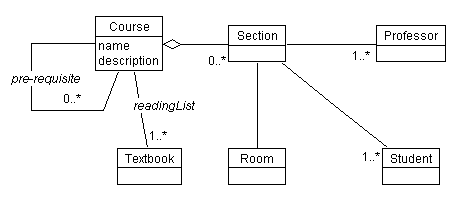
Class diagram for Course
There is one analysis class card for each class discovered during the use-case-analysis workshop.
![]()